Federate resource management in a Distributed Virtual Environment
O. Belmonte, M. Castañeda, D. Fernández, J. Gil, S. Aguado, E.
Varella, M. Nuñez, J. Segarra
Ó. Belmonte, et al., Federate resource management in a Distributed Virtual Environment, Future Generation Computer Systems (2009),
doi:10.1016/j.future.2009.08.014
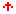
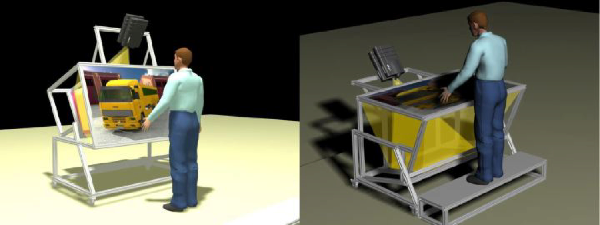
Most Distributed Virtual Environments use ad hoc protocols to share resources and synchronize interaction over a common virtual world. In this scenario, it is dificult to use new virtual reality devices if they have not been taking into account since the beginning. This paper shows how to manage virtual reality devices as federate resources in a virtual world using the HLARTI standard architecture. This approach has been used as a framework to build simulators for training workers in civil engineering.
Efficiently Using Connectivity Information between Triangles in a Mesh for Real-Time Rendering
O. Belmonte, I. Remolar, J. Ribelles, M. Chover, M. Fernández,
Future Generation Computer Systems, Special issue on Computer Graphics and Geometric Modeling, vol. 20:8, 1263-1273, November 2004. ISSN 0167-739X
Triangle meshes are the most popular standard model used to represent polygonal surfaces. Drawing these meshes as a set of independent triangles involves sending a vast amount of information to the graphics system. Taking advantage of the connectivity information between the triangles in a mesh dramatically diminishes the amount of information the graphics system must handle. Multiresolution Triangle Strips (MTS) represent a triangle mesh as a collection of multiresolution triangles strips. These strips are the basis of both the storage and the rendering stage. The coherence between the extraction of two levels of detail is used in the model in order to decrease the visualisation time.
Multiresolution modeling of arbitrary polygonal surfaces: a characterization
J. Ribelles, A. López, O. Belmonte, I. Remolar, M. Chover,
Computers & Graphics, vol. 26:3, 449-462, June 2002. ISSN 0097-8493
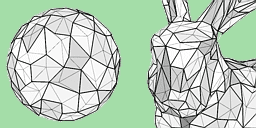
Recent technological advances have favored the apparition of highly detailed objects and, consequently, their availability for a wide diversity of applications. Normally, these objects are represented by means of complex polygonal surfaces formed by hundreds of thousands of polygons, which produce important increases in the costs of storage, transmission and visualization. Multiresolution modeling, which allows an object to be represented by means of a set of approximations, each with a different number of polygons, has been successfully presented as a solution for the efficient manipulation of this type of objects. Although the first references to multiresolution modeling appeared more than 20 years ago, most of the multiresolution schemes specifically applied to polygonal surfaces have been proposed recently. This paper, after a brief review of multiresolution modeling, presents a characterization of the most interesting multiresolution schemes for arbitrary polygonal surfaces. The objective is to make the similarities and differences between them easily visible. With this aim, a series of characteristics is enumerated. These characteristics have commonly been used to define the multiresolution schemes and they are arranged together depending on whether they refer to the applications, to the input data or to the internal operation.